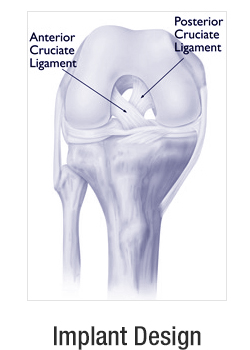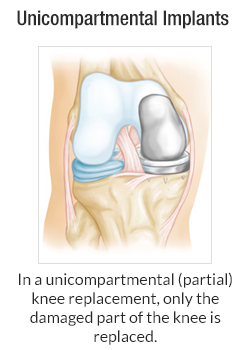
There are many different types of implants. The brand and design used by your doctor or hospital depends on many factors, including:
- Your needs, based on your knee problem and knee anatomy, as well as your age, weight, activity level, and general health.
- Your doctor’s experience and familiarity with the device.
- The cost and performance record of the implant.
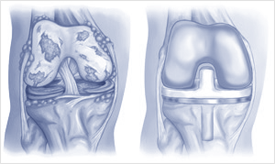
- Your surgeon will discuss with you the type of implant that will be used for your knee replacement surgery.
- In total knee replacement, damaged bone and cartilage are removed and replaced with metal components that recreate the surface of the joint.

IMPLANT COMPONENTS
What is meant by Implant Components?
Implants are made of metal alloys, ceramic material, or strong plastic parts. Up to three bone surfaces may be replaced in a total knee replacement:
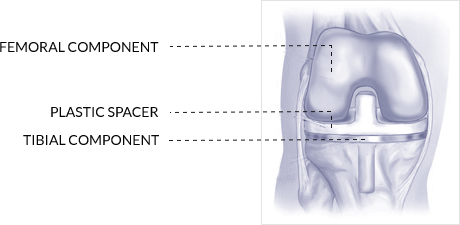
- The lower end of the femur: The metal femoral component curves around the end of the femur (thighbone). It is grooved so the kneecap can move up and down smoothly against the bone as the knee bends and straightens.
- The top surface of the tibia: The tibial component is typically a flat metal platform with a cushion of strong, durable plastic, called polyethylene. Some designs do not have the metal portion and attach the polyethylene directly to the bone. For additional stability, the metal portion of the component may have a stem that inserts into the center of the tibia bone.
- The back surface of the patella: The patellar component is a dome-shaped piece of polyethylene that duplicates the shape of the patella (kneecap). In some cases, the patella does not need to be resurfaced.
Types of Tibial Components
- FIXED BEARING IMPLANTS
Most patients get a fixed-bearing implant. In this design, the polyethylene of the tibial component is attached firmly to the metal implant beneath. The femoral component then rolls on this cushioned surface.
- MOBILE-BEARING IMPLANTS
In a mobile-bearing knee the polyethylene insert can rotate short distances inside the metal tibial tray. This is designed to allow patients a few degrees of greater rotation to the medial and lateral sides of their knee.
- FIXED-VS. MOBILE BEARING IMPLANTS
DURABILITY. In some cases, excessive activity and/or extra weight can cause a fixed-bearing prosthesis to wear down more quickly. Worn components can loosen from the bone and cause pain. Loosening is a major reason some artificial joints fail.
If you are younger, more active, and/or overweight, your doctor may recommend a rotating platform/mobile-bearing knee replacement. Although these implants have been designed for potentially longer performance with less wear, research has not yet established improved durability or function with mobile-bearing implants.
SOFT-TISSUE SUPPORT. Mobile-bearing knee implants require more support from soft tissues, such as the ligaments surrounding the knee. If the soft tissues are not strong enough, mobile-bearing knees are more likely to dislocate.
COST. Mobile-bearing implants may cost more than fixed-bearing implants.
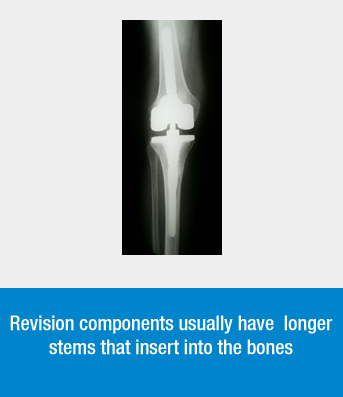
Revision Components
- How long a knee replacement lasts, depends on several factors, including activity level, weight, and general health. Just as wear in the natural joint contributed to the need for a replacement, wear in the implant may eventually require a second surgery (called a joint revision).
- In a revision procedure, some or all of the parts of the original implant are removed and replaced with new components.
- Revision components typically have longer stems which fit into the femur and tibia. They may also have attached metal pieces called augments which substitute for missing bone.
- Revision components often have a cam in the center of the knee similar to a posterior stabilized component. In revision components, though, the cam is larger to give the knee more stability.
- In cases where the knee is very unstable and a large amount of bone is missing, it may be necessary to join the femur and tibia with a metal “hinge” in the center.